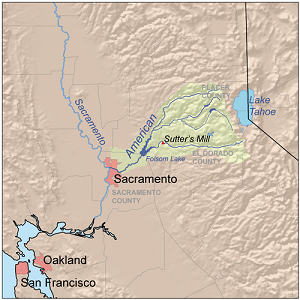
The American River runs from
the Sierra Nevada to the San Joaquin Valley, eventually emptying into San
Francisco Bay and the Pacific Ocean.
History The Maidu peoples inhabited the American River
for thousands of years before foreigners settled the region. They utilized the
vast river resources for shelter, clothes, baskets, and other goods.
The California Gold Rush started in 1848 when gold was found on the
American River. The South Fork in particular was a top destinations for early
miners.
River
Forks the American River is divided into the North, Middle, and
South forks; the three forks originate in the Lake Tahoe area. All three forks
are known for their verdant canyons, forested ridges, massive rock formations,
trails, winter adventures, snowy peaks, fishing and white water rafting. Fish
species that live within the American River include the Chinook salmon and
Steelhead Trout.
American
River Parkway below Folsom Lake, the river passes through an urban
area and riparian park containing fishing and family-oriented rafting, paved
bicycling and multi-use trails. Also, Leidesdorff Ranch, a 35 thousand acre - 140 km2
- cattle and wheat agribusiness.
Your anchor locations when visiting Northern California include Lake Tahoe, Sacramento, Sonoma and San Mateo Counties near San Francisco Bay
Ecosystem
the climate of the California American River is Mediterranean; rainy winters
and very dry summers. The region is prone to seasonal drought conditions.
Sacramento County is known for its cool winters, and hot summers, with low
average precipitation. Much of the Central Valley was historically wetlands,
which made the ground very fertile and attractive for agriculture. The American
provides Sacramento County with its main source of drinking water and houses a
multitude of plants and wildlife, creating an immensely bio diverse ecosystem.
The
American River Conservancy works to conserve the wildlife, aquatic
and terrestrial habitats and resources around the American River watershed. The
land they protect helps the American River water quality by conserving and
resorting wet meadows, wetlands, and riparian areas. It also preserves the
cultural and historic values of the river systems and surrounding landscapes.
Recreation whitewater rafting; the South Fork has Class III rapids, the Middle Fork has Class IV rapids, and the North Fork has Class IV spring run-off rapids. All three rivers also feature Class II sections.